A novel LNP formulation that allows for the conjugation of a chemotherapeutic agent to small interfering RNA (siRNA)-loaded LNP.
Problem:
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) accounts for ~4% of all cancers, making it one of the most common cancers in the United States. Most NHL arises from B cells, and insufficient response to treatments is primarily a result of resistance to apoptosis/cell death, with B-cell leukemia/lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) protein being a major anti-apoptotic factor. Attempts to combine a Bcl-2 oligonucleotide therapeutic, such as Bcl-2 siRNA (siBcl-2) and doxorubicin (DOX), a pro-apoptotic chemotherapeutic agent is being made. While LNPs can effectively encapsulate siRNA and facilitate its intracellular delivery, the challenge remains for delivering both siRNA and a chemotherapeutic drug, such as DOX.
Solution:
Creating siBcl-2 LNP2-DOX, which has the (6-maleimidocaproyl) hydrazone derivative of DOX (DOX-EMCH) conjugated to thiolated LNP loaded with siBcl-2, allows for the co-delivery of siBcl-2 and DOX.
Technology:
The inventors introduced free thiol groups to LNPs and, by microfluidic mixing, created thiolated LNPs containing siBcl-2. DOX-EMCH, a clinical prodrug of DOX, possessing a maleimide group and an acid-cleavable hydrazone bond that can bind albumin (which prolongs DOX-EMCH’s half-life and releases DOX in an acidic environment such as the endosome), was then directly conjugated to siBcl-2 LNPs via a thiol-maleimide Michael addition click reaction.
Advantages:
- Downregulation of Bcl-2 protein level to 55% of the control group’s level in Burkitt’s lymphoma (Raji) cells
- Reduction in cell viability to 60% with the lowest tested concentration (25 nM), and to 20% and 6% with 50 nM and 100nM (highest dose), respectively
- Half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 25.64 nM at 48 hours
- Tumor growth suppression and no significant weight loss and abnormal behavioral changes were seen in mice after 11 days of treatment
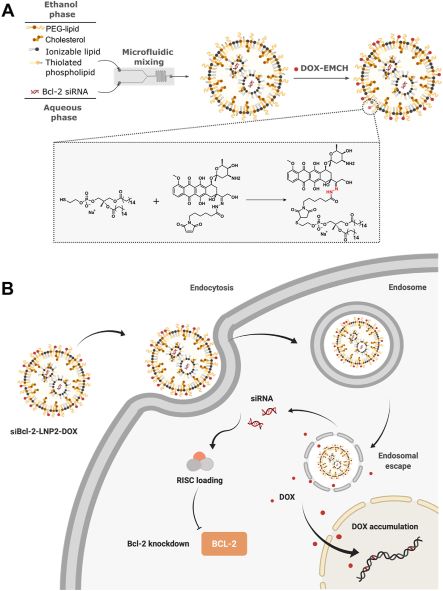
(A) A schematic illustrating the preparation of doxorubicin-conjugated Bcl-2 siRNA-loaded lipid nanoparticles (siBcl-2 LNP2-DOX). LNPs were formulated by microfluidic mixing, followed by conjugation with DOX through a thiol-maleimide Michael addition click reaction between DOXO-EMCH and thiolated phospholipid PTE. (B) Schematic diagram of intracellular co-delivery of siBcl2 and DOX enabled by siBcl-2 LNP2-DOX. Figure obtained from Published manuscript by Butowksa et al., titled “Doxorubicin-conjugated siRNA lipid nanoparticles for combination cancer therapy.”
Stage of Development:
- Target Identified
- Preclinical Discovery
Intellectual Property:
- US Provisional Application Filed
Case ID:
22-9995-tpNCS
Web Published:
10/30/2023
Patent Information:
| App Type |
Country |
Serial No. |
Patent No. |
File Date |
Issued Date |
Expire Date |